Biotin is also known as Vitamin B7 or Vitamin H, and is classified as a water soluble vitamin. It occurs in a wide variety of foods such as egg yolk, liver and some cereals. The vitamin is also synthesized by bacteria found in the human gut.
It is considered readily available and therefore Biotin deficiency rarely occurs unless for individuals who are severely malnourished, and sometimes late on in pregnancy. There are also intestinal conditions that can make Biotin unavailable for use by inhibiting its absorption in the digestive tract.
Active Components in Biotin
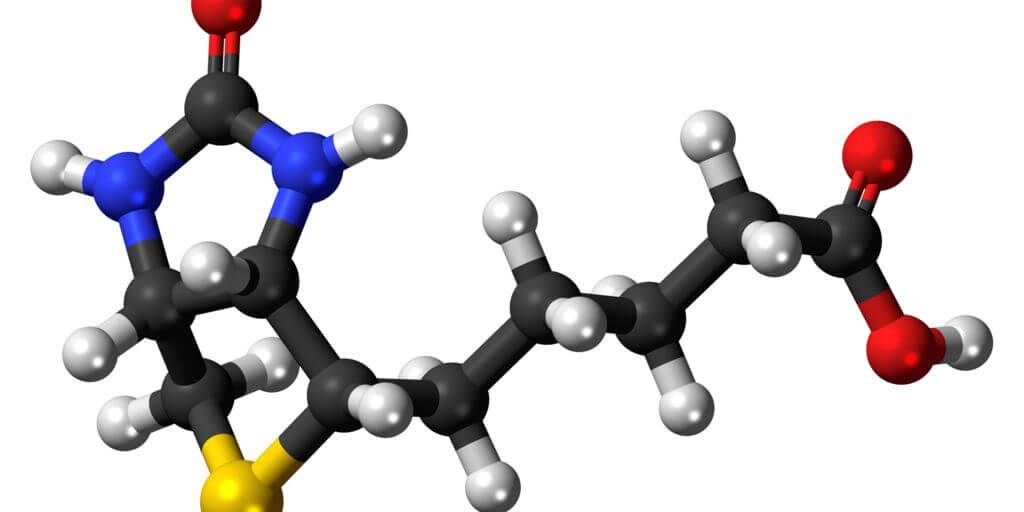
Biotin is a heterocyclic compound that consists of an Imidazole ring that is joined to a Tetrahydrothiophene ring. Tetrahydrothiophene possesses a Valeric Acid side chain. There are eight theoretically possible Biotin stereoisomers. From amongst the eight, only the D-(+)-Biotin stereoisomer is found in nature. It is known as an enzyme cofactor as it binds to and activates the five carboxylase enzymes found in humans.
Effects of Biotin Deficiency
As mentioned, Biotin acts as a coenzyme in our bodies, supporting the function of the carboxylase enzymes. Since carboxylase enzymes are involved in gluconeogenesis, amino acid metabolism and fatty acid synthesis, Biotin deficiency affects energy metabolism and other physiological processes in the body.
Biotin deficiency also compromises the immune system and reduces the synthesis of collagen tissue. Collagen tissue is known for its role in skin elasticity among other functions. Biotin deficiency, therefore, is associated with dermatological conditions such as Psoriasis, seborrheic Eczema, Neuritis and the occurrence of opportunistic infections.
Recent reports indicate that Biotin levels in pregnant women seem to decrease as as pregnancy progresses, hence Biotin deficiency can be found in heavily pregnant women. Biotin deficiency in pregnant women can affect foetal development, as can malnutrition in general.
Symptoms of Biotin Deficiency
Biotin deficiency in both children and adults manifests in various forms that include:
Hair loss
Dry and scaly skin
Scaly rashes around the mouth and the eyes
Depression
Fatigue
Brittle nails
Infants and Biotin
In most cases, children born with milk allergies or those who can’t be breastfed, are usually fed with special therapeutic milk. Most of the therapeutic milk formulations contain tiny amounts of Biotin and others don’t contain any Biotin at all. This means that infants feeding on these formulas don’t get the required amount and may develop Biotin deficiency.
The digestive system of the infants is also immature and may not have developed the bacteria necessary to synthesise Biotin. It has been found that the serum Biotin levels for children with milk allergies are usually half that of the normal infants. Biotin deficiency in children is associated with reduced skin formation resulting in skin that is susceptible to external stimuli. This explains why some children are more vulnerable to diaper rashes than others.
Diabetes and Biotin
Palmoplantar pustular osteoarthropathy and palmoplantar pustulosis are two skin conditions characterized by pustules and rashes on the palms and soles of the feet. According to research, 60% of the individuals suffering from these conditions were diagnosed with diabetes. Increased oral administration of Biotin not only eliminated the rashes and pustules, it also lowered blood sugar significantly.
Biotin as a Supplement
In Europe and the USA, Biotin supplements are available in the form of capsules or tablets and the product has gained a lot of popularity over the years. Some other countries are yet to approve the use of Biotin as a food supplement. Most of these countries have denied approval not because of its toxicity but because of doubts about its importance as a supplement.
The recommended dietary intake of Biotin for infants and children is between 10 to 30 (mcg) while that for adults are between 30 to 100 (mcg). There is no maximum amount set for daily Biotin intake since studies show no side effects for variations of up to 100 (mcg).
Shopping
| Visit the new SHOPPING page for a wide selection of amazing products! |
Always take care when taking herbs and Read Our Disclaimer.
Biotin Herb Notes / Side Effects
Biotin has been classified as a safe and non-toxic vitamin that can be used by any group of individuals. No side effect has been associated with biotin even at higher doses. However, just like any other supplement, it is advisable to consult with your doctor before you start on any supplement especially when you:
Have been in a long-term treatment with antibiotics
Smoke cigarettes
Take medication for seizures
On dialysis
Eat more than two raw egg whites per day

 I cover my greys with a custom ginger blend from
I cover my greys with a custom ginger blend from 
Leave a Reply